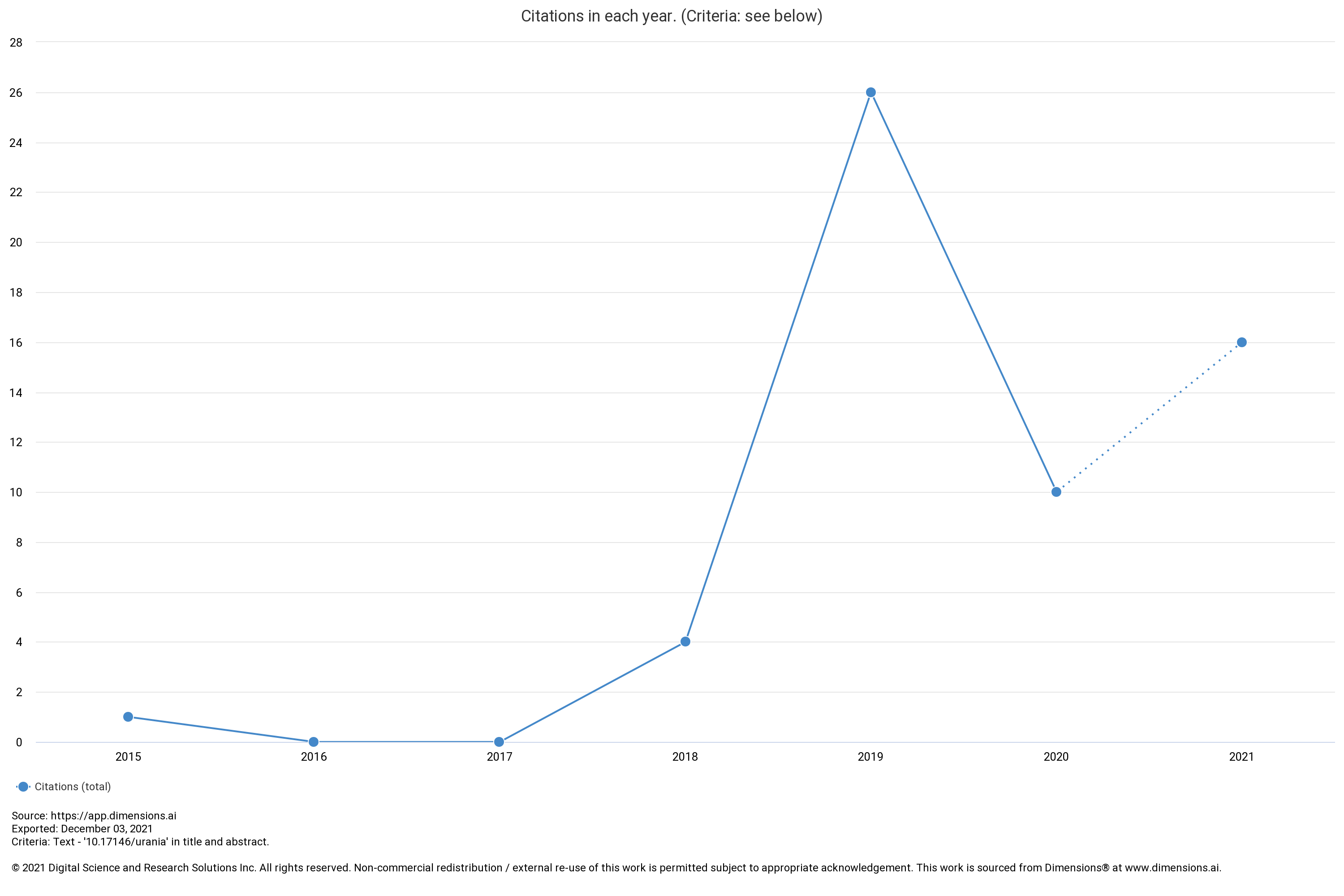
IMPROVEMENT OF PLASMA ELECTROLYTIC OXIDATION (PEO) COATING ON ZIRCONIUM ALLOYS USING ADDITIVES FOR NUCLEAR FUEL CLADDING APPLICATION
Sari
This study explores the improvement of Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation (PEO) coatings on zirconium alloys using additives for pressured water reactor (PWR) fuel cladding application. PEO is a promising surface treatment for zirconium alloys, offering improved corrosion and wear resistance, essential for applications in extreme environments, such as nuclear reactors. Various types of stable particle and dissolved additives were incorporated into the electrolyte during PEO process to modify the coating's microstructure, phase composition, and mechanical properties. The incorporation of stable particle such as Al₂O₃, CeO₂, and Y₂O₃ not only reduces surface porosity and roughness but also increases the presence of the tetragonal zirconia phase (t-ZrO₂), leading to enhanced corrosion and wear resistance. Additionally, the use of dissolved additives, including complex agents and salts, positively affected plasma characteristics and further improved coating density and durability.
Keywords: Plasma Electrolytic Oxidation, zircaloy, additives, corrosion
Teks Lengkap:
PDFRefbacks
- Saat ini tidak ada refbacks.
Penerbit: Pusat Riset Teknologi Bahan Nuklir dan Limbah Radioaktif
Diindeks oleh: